MedPAC Commissioners Recognize Importance of Ground Ambulance Services and Complexities of AFS
Please either or Join!
Written by Kathy Lester on . Posted in Cost Data Collection, Cost Survey, Medicare, News.
Written by Kathy Lester on . Posted in Cost Data Collection, Member Advisories, News.
Written by AAA Staff on . Posted in Advocacy Priorities, Government Affairs, Legislative.
Last night, the United States Senate passed language as part of the FY 2022 Omnibus Appropriations Package that would delay the due date of the Medicare Payment Advisory Committee (MedPAC) report analyzing ambulance cost data. The U.S. House of Representatives had passed the package on Wednesday. The delay in the MedPAC report is a victory for the AAA and our members as we spearheaded efforts for the delay.
We thank Senators Chuck Schumer, Catherine Cortez Masto, Ron Wyden, Mike Crapo and Debbie Stabenow and Representatives Richard Neal, Kevin Brady, Frank Pallone and Catherine McMorris Rogers for championing and assisting with passage of the provision.
The delay in the timing of the MedPAC report was necessary due to CMS postponing the beginning of ambulance cost data collection by two years to account for the COVID-19 pandemic. Even though data collection had been delayed, MedPAC indicated that they were compelled to stick to the statutory deadline of issuing a report – with very little or no new ambulance data – to Congress by March 15, 2023.
With little to no new data, MedPAC would have likely reinstated their recommendations from their 2002 ambulance report which did support most of the temporary ambulance increases but at the cost of cutting BLS non-emergency services by 5.75%. MedPAC had also recommended doing away with rural and super rural increases in favor of a low volume adjuster which would disrupt reimbursement levels for rural providers without having more detailed data if indeed the proper approach.
The language from the FY2022 Omnibus Appropriations Package is as follows:
SEC. 311. REVISION OF THE TIMING OF MEDPAC REPORT ON AMBULANCE COST DATA.
Section 1834(l)(17)(F)(i) of the Social Security Act (42 U.S.C. 1395m(l)(17)(F)(i)) is amended by striking ‘‘Not later than March 15, 2023, and as determined necessary by the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission thereafter’’ and inserting ‘‘Not later than the second June 15th following the date on which the Secretary transmits data for the first representative sample of providers and suppliers of ground ambulance services to the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission, and as determined necessary by such Commission thereafter,’’.
Next week, we will be launching a Call to Action asking AAA members to reach out to their members of Congress to cosponsor the Protecting Access to Ground Ambulance Medical Services Act (H.R. 2454, S. 2037) Medicare Ambulance which would extend the temporary Medicare ambulance increases for five years. The increases expire at the end of this year and the five-year extension is necessary to provide time for the MedPAC report and the Congress to act.
Written by Kathy Lester on . Posted in Medicare, Member Advisories, Member-Only, Regulatory, Reimbursement.
During its October meeting, the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC), reviewed Medicare’s current policies related to non-urgent and emergency care, as these topics relate to the use of hospital emergency departments (EDs) and urgent care centers (UCCs). The Commission is examining this topic because the use of ED services in recent years has grown faster than that of physician offices. At the same time, the share of ED visits that are coded as high acuity has increased.
The Commission is exploring Medicare beneficiaries’ use of EDs and UCCs for non-urgent services. In addition, the Commission is analyzing ED coding to determine if the increase in coding high-acuity visits reflects real change in the patients treated in EDs. This slide deck shows the potential savings Medicare could realize if beneficiaries shift certain care to the UCC setting.
During the meeting, the staff sought feedback from Commissioners for developing next steps. This topic will likely continue to be addressed in future meetings.
From the perspective of ambulance payment reform, the observations made by the Commissioners and staff would also seem to support incorporating scope-appropriate ambulance services in the context of community paramedicine or treatment at the scene with referral. While additional work needs to be done by the ambulance community before these services can be incorporated into the Medicare reimbursement program, discussions like the one at MedPAC last week, show the importance of getting the details right so that ambulance services can be part of new payment models likely to be considered.
The American Ambulance Association is leading the effort with the Medicare program to develop appropriate models that account for the cost of providing services through sustainable reimbursement rates, rather than the use of temporary grants. We are also focused on ensuring services align with the scope of practice laws. Led by the Payment Reform and the Medicare Regulatory Committees, our efforts include regular meetings and discussions with leaders at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, as well as key Members of Congress. Follow us on Facebook and Twitter to learn more about our ongoing efforts.
Written by Brian Werfel on . Posted in Advocacy Priorities, Member-Only, News, Reimbursement, Talking Medicare.
On October 1, 2018, CMS implemented an additional thirteen (13%) cut in reimbursement for non-emergency BLS transports to and from dialysis. This cut in reimbursement was mandated by Section 53108 of the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018. This on top of a ten (10%) cut in reimbursement for dialysis transports that went into effect on October 1, 2013. As a result, BLS non-emergency ambulance transports to and from dialysis that occur on or after October 1, 2018 will be reimbursed at 77% of the applicable Medicare allowable.
In related news, CMS has released its national payment data for calendar year 2017. This data shows a continued reduction in total Medicare payments for dialysis transports. Medicare paid $477.7 million on dialysis transports in 2017, down from $488.9 million in 2016. This continues a downward trend that has seen total payments decline from a high of more than $750 million in 2013 (see accompanying chart to the right). Not coincidentally, it was in 2013 that our industry saw its first reduction in Medicare’s payments for dialysis transports.
The payment reduction is partially the result of the reduction in the amounts paid for dialysis services. However, it is also reflective of an overall decline in the number of approved dialysis transports. For this, we can look primarily to the impact of a four-year demonstration project that requires prior authorization of dialysis transports in 8 states and the District of Columbia.
As a reminder, the original prior authorization states were selected based on higher-than-average utilization rates and high rates of improper payment for these services. In particular, the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) had singled out these states as having higher-than-average utilization of dialysis transports in a June 2013 report to Congress. The chart below shows total spending on dialysis in those states in the years immediately preceding the implementation of the prior authorization project up through 2017, the third year of the demonstration project. While the three states had very different trajectories prior to 2015, each showed a significant decrease in total payments for dialysis under the demonstration project.
However, it is the trajectory of these changes that I want to discuss in this month’s blog. In previous blogs, I discussed the impact of the particular Medicare Administrative Contractor on the outcomes under prior authorization. Specifically, I noted that, while dialysis payments dropped in each state, the decline was far more dramatic in the states administered by Novitas Solutions (NJ, PA) than in the South Carolina, which was administered by Palmetto GBA. This trend continued in the second year of the program, which saw prior authorization expanded into five additional states and the District of Columbia. Those states administered by Novitas (DE, MD) saw far greater declines than the states administered by Palmetto (NC, VA, WV).
Given these declines, the data from the third year is somewhat surprising. The states administered by Palmetto continued to see declines in total dialysis payments, with the only exception being West Virginia. However, in the states administered by Novitas, we saw total dialysis payments increase, particularly in New Jersey, which saw nearly a 33% increase in total dialysis payments.
Three years into the prior authorization program, it is starting to become clear that the two MACs have approached the problem of overutilization of dialysis transports using two different approaches. Palmetto appears to have adopted a slow-and-steady approach, with total payments declining in a consistent manner year after year. By contrast, Novitas adopted more of a “shock the system” approach, where it rejected nearly all dialysis transports in the first year, and has adopted a somewhat more lenient approach in subsequent years.
Last year, I wrote that two years of data under the prior authorization program permitted two conclusions: (1) the implementation of a prior authorization process in a state will undoubtedly result in an overall decrease in the total payments for dialysis within that state and (2) the size of that reduction appears to be highly dependent on the Medicare contractor.
With an additional year of data, I think both conclusions remain valid, although I would revise the second to suggest that the initial reduction has more to do with the Medicare contractor. The evidence from the third year of the program suggests that the trends tend to equalize after the first few years. It is also possible that Novitas felt a more aggressive approach was needed in the first few years to address evidence of widespread dialysis overutilization in the Philadelphia metropolitan area.
This has potential implications beyond the demonstration project, as CMS looks towards a possible national expansion of the program. Among other issues, it suggests that the AAA must continue its efforts to work with CMS and its contractors on developing more uniform standards for coverage of this patient population.
The AAA continues to work on legislation that would restructure this cut to dialysis transport reimbursement. The AAA strongly supports the NEATSA Act (H.R.6269) introduced by Congressman LaHood (R-IL) and Congresswoman Sewell (D-AL) that would restructure the offset so that a majority of the additional reduction would be focused on those ambulance service agencies in which 50% or more of their volume are repetitive BLS nonemergency transports. AAA members and the AAA are working to get a Senate companion bill introduced shortly. The goal of this legislation would be to have the restructured offset go into effect as soon as possible. Thank you to the dozens of AAA members who have already contacted their members of Congress voicing their support for this critical legislation.
Have an issue you would like to see discussed in a future Talking Medicare blog? Please write to me at bwerfel@aol.com
Written by Brian Werfel on . Posted in Medicare, Talking Medicare.
On February 28, 2018, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) posted an interim report on its prior authorization demonstration project for repetitive, scheduled, non-emergent ambulance transportation. The report, titled First Interim Evaluation Report of the Medicare Prior Authorization Model for Repetitive Scheduled Non-Emergent Ambulance Transport (RSNAT), was conducted by Mathematica Policy Research, a nonpartisan think tank. Mathematica studied the impact of the prior authorization model on Medicare payments, ambulance utilization, and patient quality of care.
CMS implemented the prior authorization demonstration project in December 2014 in three states: New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and South Carolina (referred to in the report as “Year 1 States”). These states were selected based on higher-than-average utilization rates and high rates of improper payment for these services. The Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA) subsequently expanded the demonstration project to five additional states (Delaware, Maryland, North Carolina, Virginia, and West Virginia) and the District of Columbia on January 1, 2016 (referred to in the report as “Year 2 States”).
The goal of the demonstration project was to study the impact of prior authorization on the utilization of ambulance transportation. Under the program, ambulance suppliers in the affected states would be required to submit documentation related to medical necessity to their Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs) prior to Medicare payments being authorized. The MACs would review this documentation, and approve those they felt were medically necessary, while denying those patients that they believed could be safely transported by other means.
Mathematica was retained by CMS to conduct a five-year evaluation of the impact of the RSNAT prior authorization model. Specifically, Mathematica was asked to evaluate the program on five specific measures:
Mathematica indicated that it conducted its review using both quantitative and qualitative data analysis. It analyzed data from January 2012 through June 2016. Mathematica noted that it estimated program effects by measuring the change over time in certain key metrics between the pre-model years (2012 through 2014 for Year 1 States, 2012 through 2015 for Year 2 States) and post-implementation years (2015 through 2016 for Year 1 States, 2016 for Year 2 States) in the nine model states. It also compared these states against non-model states.
Because dialysis patients account for more than 75% of all repetitive transports, the report focused on ESRD patients.
The study concluded that the RSNAT prior authorization model successfully reduced the utilization of ambulance, as well as Medicare’s expenditures on repetitive ambulance transportation. The report indicated that a reduction of nearly 70% in the nine states combined. This was associated with an approximately $171 million reduction in Medicare payments for dialysis transports. Interestingly, the study concluded that it also led to a reduction in total Medicare FFS expenditures for ESRD beneficiaries.
Not surprisingly, the Year 1 States saw more dramatic reductions than the Year 2 States. Mathematic attributed this to the fact that the Year 1 States were specifically selected based on higher-than-average utilization rates, while the Year 2 States were selected based on their geographic proximity to the Year 1 States. Mathematic concluded that national expansion would likely result in additional reductions in Medicare payments, but that the impact would likely be less than what was seen with the Year 1 States.
With respect to issues related to access and quality of care, Mathematica found little quantitative evidence to suggest that prior authorization had a negative impact on quality or access to care. The authors noted that they defined a negative impact quite narrowly, limiting it to emergency department visits, emergency ambulance utilization, unplanned hospital admissions, and death. The study did note a 15% increase in emergency dialysis use, which the authors noted might suggest that some beneficiaries were delayed in receiving ESRD treatment. The authors further noted that some beneficiaries who were denied approval could experience difficulty in accessing alternative means of transportation. Finally, the study did note that stakeholders, including ambulance suppliers, expressed concerns that some beneficiaries may have turned to other services — including emergency ambulance transportation and ED services — in response to being turned down for ambulance transportation.
The study indicated that the MACs reported that they successfully implemented the prior authorization model, and that they have adequate staffing to ensure that they meet CMS’ timelines for responding to prior authorization requests. The MACs did note, however, that there were some difficulties in implementing the program in the Year 1 States, which they attributed to their underestimating the required amount of training. The MACs self-reported that they did far better implementing the program in the Year 2 States.
The impact on the ambulance supplier community was mixed. Mathematica noted a 15% decrease in the number of ambulance suppliers per 100,000 beneficiaries in the model states after implementation. The majority of the ambulance suppliers that (euphemistically) “left the program” were smaller services that specialized in dialysis transports. Other companies reported that they reduced their volume of dialysis transports, or stopped transporting dialysis patients entirely. Not surprisingly, the ambulance supplier community believed that the coverage standards being used by the MACs were too strict.
Finally, Mathematica indicated that it was difficult to determine the prior authorization model’s impact on improper payments. This was partly due to the fact that improperly paid claims for ambulance services increased in both the model states and non-model states during the review period.
Mathematica’s findings do not come as a surprise. Rather, they pretty much confirm what our industry has long recognized. The HHS Office of the Inspector General has long warned that dialysis transports are susceptible to overutilization. The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) concluded the same thing in a June 2013 report to Congress.
Moreover, the A.A.A. has acknowledged the potential for fraud and abuse in connection with these transports. It was for this precise reason that the A.A.A. pushed for prior authorization as a better alternative to reductions in Medicare’s payment for dialysis transports. Our position was that payment reductions failed to adequately address the underlying incentives for overutilization, and, therefore, primarily punished the legitimate providers of such transports.
To its credit, Mathematica acknowledged that factors other than the ambulance suppliers’ financial motives contribute to overutilization. Specifically, it cited the difficulty many beneficiaries face in accessing alternative means of transportation, even where such alternative means would meet the patient’s medical needs. Mathematica also noted the confusion that exists among other health care providers, particularly physicians, in terms of when Medicare would cover an ambulance. Long term, my hope is that this acknowledgement will pave the way towards more constructive conversations between the industry and Congress, CMS, and other stakeholders.
In the short term, the report clears a statutory hurdle that has prevented CMS from considering the expansion of the prior authorization model to the rest of the nation. It remains to be seen whether CMS believes this report is sufficient to make a determination on national expansion, or whether CMS will want to see additional evidence.
Have an issue you would like to see discussed in a future Talking Medicare blog? Please write to me at bwerfel@aol.com.
Written by Brian Werfel on . Posted in Medicare, Member-Only, Talking Medicare.
Novitas Solutions, Inc. recently announced that it will no longer issue prior authorizations for scheduled, repetitive non-emergency transports, effective December 1, 2017. This announcement was based on Novitas’ expectation that the demonstration project will expire at the end of this calendar year. For ambulance suppliers in the states that currently operate under prior authorization, the focus invariably turns to what that means for their repetitive patient populations?
First a little background. In May 2014, CMS announced the implementation of a three-year prior authorization demonstration project for repetitive scheduled non-emergency ambulance transports. This demonstration project was initially limited to the states of New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and South Carolina. These states were selected based on higher-than-average utilization rates and high rates of improper payment for these services. In particular, the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) had singled out these states as having higher-than-average utilization of dialysis transports in a June 2013 report to Congress. As initially conceived, the prior authorization demonstration project first went into effect on December 15, 2014.
Congress subsequently elected to expand this demonstration project to additional states as part of the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA). Specifically, Congress mandated that the program be expanded to six additional states (Delaware, Maryland, North Carolina, Virginia, and West Virginia) and the District of Columbia by January 1, 2016, and then potentially to the rest of the nation by January 1, 2017. However, CMS never issued the required report; as a result, the contemplated national expansion never occurred.
If you operate in a state that is not currently operating under prior authorization, the answer to this question is relatively straightforward, i.e., nothing will change.
If, however, operate in a state that is currently subject to prior authorization, this question is a bit trickier. What we do know is that the actual mechanics of submitting claims will revert to the same process you experienced prior to the implementation of prior authorization. You will submit claims for repetitive patients directly to the Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC), who will likely process them in same manner they process other Medicare claims. In other words, 14 days after the submission of the claim, you will likely receive a remittance notice indicating that the claim has either been paid or denied.
We also know that you will no longer benefit from the protections against post-payment review of these claims. Under the prior authorization model, CMS made clear that it would not audit claims paid based on a valid authorization, except in instances where it could demonstrate that the prior authorization was fraudulently procured.
What we don’t know is whether the MACs will implement any temporary measures to guard against ongoing over-utilization and/or fraud. To better understand what I mean, put yourself in the position of the MAC. You have empirical evidence (see the chart to the right) that prior authorization has resulted in dramatic reductions in the amount of Medicare dollars paid for dialysis transports. You have further seen little evidence that this reduction in payments has resulted in any serious access to care issues.
The logical conclusion you would draw is that the amounts paid for dialysis prior to the implementation of prior authorization were likely excessive. If so, you might consider some proactive steps to prevent dialysis utilization from increasing back to the levels seen prior to the implementation of prior authorization.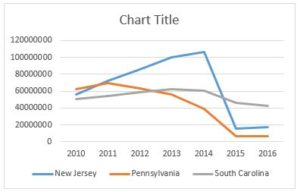
So, it is possible (perhaps even likely) that ambulance suppliers in some of these states may see their MAC elect to implement prepayment reviews for dialysis patients. This could be similar to the process Novitas used for the initial three round trip transports to dialysis.
I also think it is reasonable to expect that the MACs, the Zone Program Integrity Contractors, and the OIG will monitor utilization trends, with an eye towards conducting post-payment reviews on ambulance suppliers that see their dialysis volume increase sharply next year.
In the previous section, I touched on the steps Medicare and its contractors might take to prevent a return to pre-prior authorization levels of dialysis utilization. In this section, I want to talk about some of the knock-on effects ambulance providers are likely to see.
One of the more interesting changes we saw in the prior authorization regime was a re-balancing of the power dynamic between ambulance suppliers and facilities, i.e., assisted living facilities and skilled nursing homes. Prior to the implementation of prior authorization, that power dynamic was slanted heavily in favor of the facility. By that I mean they could exert tremendous pressure on ambulance suppliers to take marginal patients by ambulance. If you were involved in the industry prior to 2015, you undoubtedly heard an SNF administrator tell you something to the effect of “if your company won’t take the patient by ambulance, I can easily find another company that will.” In competitive markets, that statement was usually accurate.
Under the demonstration project, prior authorization or lack thereof traveled with the patient. What that meant is that if your ambulance company submitted a prior authorization request that was denied, that denial would apply to any other ambulance company that might be interested in taking the patient. As a result, the nursing home could no longer hold the threat of going elsewhere with their business over your head.
Prior authorization also affected the standing policies of dialysis centers. Many free-standing dialysis centers have standing policies that they will not assist in transferring the patient to and from the dialysis treatment chair. This meant that patients that could be transported in a wheelchair van, but who required assistance to transfer out of their wheelchair presented a conundrum. There wouldn’t be medical necessity for the ambulance, but there would be no easy way for you to transfer them into the treatment chair without a second crew member (something most wheelchair van services don’t offer). Under prior authorization, it was easier for the ambulance company to push back, since they knew they wouldn’t be paid for the ambulance. As a result, I have heard that dialysis employees in these states had started to assist patients in transferring.
No really, it’s true…
One potential consequence of the prior authorization going away is that it may shift this power dynamic back to the facilities, with all of the negative consequences that are likely to result.
“Okay, I get what you are saying, but what I really want to know is whether I should loosen our standards for accepting a dialysis patient or not?”
Good question. Unfortunately, not one that permits an easy answer. The implementation of prior authorization shifted the cost-benefit analysis associated with transporting dialysis patients. It was likely that you were going to have a smaller number of patients approved and paid, but you could rest easy that you wouldn’t be at risk of having to return that money years later as the result of a Medicare audit.
The expiration of prior authorization shifts the cost-benefit analysis yet again. It is likely that you have tightened up your criteria for who you accept for dialysis transportation as a result of prior authorization. Loosening those criteria would almost certainly result in an increase in your short-term revenues. However, that would be offset, to some degree, by the increased risk of a Medicare audit.
For that reason, the course of action I have been recommending to people is not to dramatically loosen your standards. Instead, I typically ask whether they currently have patients that they believe do require an ambulance, but who were rejected for prior authorization by the MAC. Most providers respond that they do. Put another way, we are trying to identify the patients that you would feel comfortable defending in an audit. That is the additional population I would target for transportation next year.
Have an issue you would like to see discussed in a future Talking Medicare Blog? Please write to me at bwerfel@aol.com.
Written by Brian Werfel on . Posted in Member-Only, News, Reimbursement, Talking Medicare.
In May 2014, CMS announced the implementation of a three-year prior authorization demonstration project for repetitive scheduled non-emergency ambulance transports. This demonstration project was initially limited to the states of New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and South Carolina. These states were selected based on higher-than-average utilization rates and high rates of improper payment for these services. In particular, the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) had singled out these states as having higher-than-average utilization of dialysis transports in a June 2013 report to Congress.
Medicare payment data from calendar year 2015 showed the effect of the demonstration project. Total spending on dialysis transports was $559 million that year, down 22% from the year before. That correlates to a cost savings to the federal government of $158 million. Telling, $137 million (86%) of those savings came from the three states that participated in the demonstration project.
The chart to the right shows total spending on dialysis in those states in the years immediately preceding the implementation of the prior authorization project up through the first year of the project. While the three states had very different trajectories prior to 2015, each showed a significant decrease in payments under the demonstration project.
We now have Medicare payment data for 2016. This blog will focus on the second year of the prior authorization demonstration project. This includes tracking the effects of prior authorization on the five additional states (DE, MD, NC, VA, and WV) and the District of Columbia, which were added to the demonstration project for 2016.
In the first year of the demonstration project, both New Jersey and Pennsylvania saw sizeable reductions (85.5% and 83.5%, respectively) in the total spending on dialysis transports. Both states saw dialysis payments rebound in 2016, with New Jersey increasing by 14.7% and Pennsylvania increasing by 3.7%. The financial community uses the phrase “dead cat bounce[1]” to describe a temporary recovery from a prolonged or pronounced decline. It is possible that explains why payments increased for these states in 2016. However, the more likely explanation is that Novitas, the Medicare Administrative Contractor in both states, recognized that the standards it used were overly restrictive during the first year of the project. If so, the increases in 2016 reflect the pendulum swinging back somewhat. If you accept that Novitas has reached an equilibrium point, total spending on dialysis in these states would be roughly 75% below pre-2015 levels.
By contrast, South Carolina saw total dialysis spending decrease by an additional 7.9% in 2016, over and above the roughly 25% reduction in 2015. Thus, spending in 2016 was roughly 30% lower than pre-2015 levels.
The follow charts track dialysis payments in the five states and the District of Columbia that were first subject to prior authorization in 2016. The chart on the left shows those states where the prior authorization project is administered by Novitas, while the chart on the right shows those states administered by Palmetto.
The phrase expresses the concept that even a dead cat will bounce if dropped from a tall enough height.
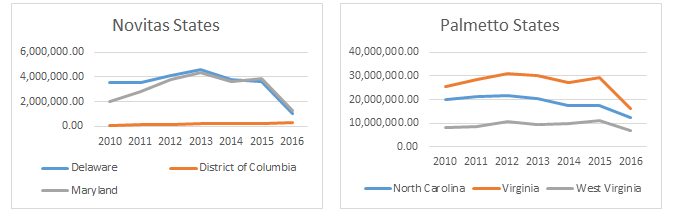
As you can see, both Delaware (72.3%) and Maryland (68.0%) showed sizeable reductions in total dialysis payments. Payments in the District of Columbia actually increased by 30%. However, a closer examination of the numbers shows that the increase was largely the result of an increase in the number of emergency transports to a hospital for dialysis, i.e., claims that fell outside the prior authorization project. Payment for scheduled BLS non-emergency transports fell 82.9% in the District, in line with reductions in the other two states.
The reductions in the Palmetto states was far more moderate, with reductions ranging from 27.8% (North Carolina) to 45.4% (Virginia). West Virginia saw a 36.0% decline.
With two years of experience under the prior authorization demonstration project, I think we can safely come to two conclusions:
The first conclusion should come as no surprise. Dialysis transports have long been the subject of scrutiny by the federal government. Moreover, the original states were not selected at random; they were selected based on data that suggested they were particularly suspect to over utilization.
The second conclusion is less intuitive. After all, Medicare coverage standards are intended to be national. While you could argue that a sizable reduction was expected for New Jersey and Pennsylvania, as there was evidence of widespread dialysis fraud in the Philadelphia metropolitan area, there was no basis to suspect widespread over utilization in Maryland or the District of Columbia. In fact, the District had only 58 BLS non-emergency dialysis transports in 2015, i.e., the equivalent of a single patient being transported for 2 months. Rather, the 2016 data suggests that Novitas has simply taken a far harder stance on dialysis than Palmetto.
This has potential implications beyond the demonstration project, which is scheduled to expire at the end of this year. As many of you know, the national expansion of prior authorization is part of the House of Representative’s ambulance relief bill (it is not mentioned in the corresponding Senate bill). The data suggests that the AAA must continue its efforts to work with CMS and its contractors on developing more uniform standards for coverage of this patient population.
Have an issue you would like to see discussed in a future Talking Medicare blog? Please write to me at bwerfel@aol.com.
[1] The phrase expresses the concept that even a dead cat will bounce if dropped from a tall enough height.
Written by Kathy Lester on . Posted in Finance, Government Affairs, Medicare, Member Advisories, Member-Only, Regulatory.
Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC or the Commission) has issued its June 2016 Report to the Congress. The June report includes recommended refinements to Medicare payment systems and identifies issues affecting the Medicare program, broader changes in health care delivery, and the market for health care services.
Chapter 7 focuses on preserving access to emergency care in rural areas. The Commission recognizes that access to inpatient and emergency services in rural areas is threatened because of the dwindling populations. Declining populations can lead to fewer hospital admissions and reduced efficiencies that can create financial and staff problems for hospitals. The Report notes that “[d]eclining volume is a concern because low-volume rural hospitals tend to have worse mortality metrics and worse performance on some process measures.” In addition, “low-volume CAHs have the difficult job of competing with each other for a shrinking pool of clinicians who want the lifestyle of operating an outpatient practice during the day, covering inpatient issues that arise at night, and covering the emergency department.”
Under current policies, most rural hospitals are critical access hospitals (CAHs). They receive a cost-based payment for providing inpatient and outpatient services to Medicare beneficiaries. To receive these payments, a hospital must maintain acute inpatient services. In rural areas, many small towns do not have a sufficient population to support such a model. Yet eliminating these services would mean giving up the supplemental payments that their hospitals receive through the CAH cost-based payment model.
The hospital prospective payment system serves as the payment model for other hospitals. Rural providers receive supplemental payments, which are also linked to providing inpatient services.
MedPAC highlights the concerns with cost-based payment models:
In light of these challenges, MedPAC sets forth a two of options that would give isolated rural hospitals the option of converting to an outpatient-only model while maintaining their special payment arrangements. These models seek to ensure access to essential services:
Under the 24/7 emergency department model, the hospital would be paid under the outpatient prospective payment rates and would receive an annual grant/fixed payment from Medicare to cover the standby costs associated with 24/7 emergency services. The current supplemental payments would be redirected to support this annual grant/fixed payment amount. If a hospital chose to use inpatient beds as skilled nursing facility (SNF) beds, it would be reimbursed under the Medicare SNF prospective payment system. The hospital could be required to use the fixed payment for emergency standby capacity, ambulance service losses, telehealth capacity, and uncompensated care in the emergency department.
Under the clinic and ambulance model, hospitals could convert their existing inpatient facilities into primary care clinics. These clinics would be “affiliated” with an ambulance service. Medicare would pay the prospective rates for primary care visits and ambulance transports. Medicare would provide an annual grant/fixed payment to support the capital costs of having a primary care practice, the standby costs of the ambulance service, and uncompensated care costs.
The Commission recognizes that the “low population density would also make it difficult to retain primary care providers and support an ambulance service.” It could also be difficult to describe the exact level of primary care and ambulance access that is required to receive the fixed Medicare payment.
MedPAC reiterates its position that “supplemental payments beyond the standard PPS rates should be targeted to isolated rural providers that are essential for access to care.” Thus, it states that a program to support stand-alone emergency departments should be limited to facilities that are a minimum distance in road miles from the nearest hospital.