GAO | Roll Out of IDR Process for Out-of-Network Claims Has Been Challenging
Fast Facts
Individuals with private health insurance can receive “surprise bills” for the difference between what a provider charged and what their insurance paid.
A 2021 law prohibits surprise billing for some services, and directed the Departments of Health and Human Services, Labor, and Treasury to give providers and insurers a forum to resolve disputes about how much insurers should pay for out-of-network care.
But the rollout has been challenging. As of June 2023, over 490,000 disputes have been submitted, a much larger number than anticipated by the agencies.
And 61% of the disputes are unresolved as of June 2023.

Highlights
What GAO Found
The No Surprises Act directed the departments of Health and Human Services (HHS), Labor, and Treasury to establish a federal independent dispute resolution process. The process, which was effective April 2022, is a voluntary forum for health care providers and health insurance issuers to resolve disputes about how much should be paid for out-of-network care. The payment determinations are made by certified dispute resolution entities, which serve as arbiters. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS)—an agency within HHS—administers the independent dispute resolution process.
The three departments reported that parties submitted nearly 490,000 disputes from April 2022 through June 2023. About 61 percent of these disputes remained unresolved as of June 2023. According to officials from the departments, a primary cause of the large number of unresolved disputes is the complexity of determining whether disputes are eligible for the process.
Number of Out-of-Network Disputes in the Federal Independent Dispute Resolution Process by Calendar Quarter, April 15, 2022—June 30, 2023
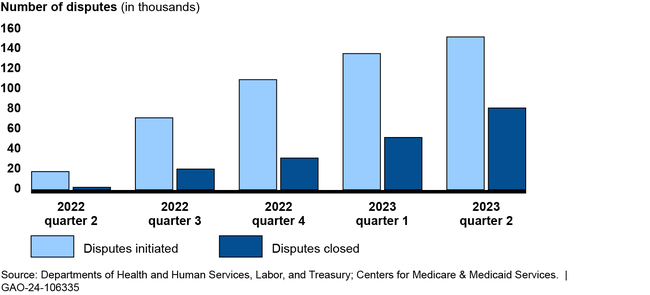
The groups GAO interviewed described a challenging roll out of the independent dispute resolution process, including a higher-than-expected dispute volume. For example, the departments anticipated about 22,000 disputes in 2022, but received nearly 490,000 through June 2023. Four groups told GAO the departments did not account for the experience of states with similar processes when making the estimate. Disputing parties and certified entities also described the broader effects of those challenges, such as backlogs resulting in delays in payment determinations. The departments have taken some actions to address challenges, such as conducting pre-eligibility reviews on submitted disputes.
To address concerns from insurers and providers, CMS and Labor look into complaints; however, stakeholder groups expressed concern with what they describe as a lack of response to submitted complaints. The departments reported limited ability to increase enforcement efforts due to budget constraints. HHS has requested a budget increase for the process, and the departments are revisiting the administrative fee amount, which is intended to cover the costs of the process, and plan to issue updated program rules.
Why GAO Did This Study
About two thirds of individuals in the United States receive their health coverage through private health plans. Balance billing is when insured patients receive a bill from a health care provider for the difference between the amount charged and the payment received from the health insurance issuer. An unexpected balance bill is referred to as a “surprise bill” and may create a financial strain for patients. For individuals with private health insurance, the No Surprises Act prohibits providers from balance billing in certain circumstances and directed the three departments to establish the federal independent dispute resolution process.
The Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021, includes a provision for GAO to review the federal independent dispute resolution process. This report describes (1) the number and types of disputes submitted between April 2022 and June 2023, and the status of their resolution; (2) selected stakeholders’ experiences with the process, and agency actions to address challenges; and (3) how federal agencies oversee the process.
GAO reviewed published reports, relevant federal laws, regulations, and guidance; and interviewed officials from CMS and Labor. GAO also interviewed five selected health care providers or their representatives, which accounted for nearly half of all submitted disputes as of December 2022. In addition, GAO interviewed three issuers, three certified entities that arbitrate the disputes, and 10 stakeholder groups.
For more information, contact John E. Dicken at (202) 512-7114 or dickenj@gao.gov.









