
Navigating a Post-Prior Authorization World
Talking Medicare: Navigating a Post-Prior Authorization World
Novitas Solutions, Inc. recently announced that it will no longer issue prior authorizations for scheduled, repetitive non-emergency transports, effective December 1, 2017. This announcement was based on Novitas’ expectation that the demonstration project will expire at the end of this calendar year. For ambulance suppliers in the states that currently operate under prior authorization, the focus invariably turns to what that means for their repetitive patient populations?
First a little background. In May 2014, CMS announced the implementation of a three-year prior authorization demonstration project for repetitive scheduled non-emergency ambulance transports. This demonstration project was initially limited to the states of New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and South Carolina. These states were selected based on higher-than-average utilization rates and high rates of improper payment for these services. In particular, the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) had singled out these states as having higher-than-average utilization of dialysis transports in a June 2013 report to Congress. As initially conceived, the prior authorization demonstration project first went into effect on December 15, 2014.
Congress subsequently elected to expand this demonstration project to additional states as part of the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA). Specifically, Congress mandated that the program be expanded to six additional states (Delaware, Maryland, North Carolina, Virginia, and West Virginia) and the District of Columbia by January 1, 2016, and then potentially to the rest of the nation by January 1, 2017. However, CMS never issued the required report; as a result, the contemplated national expansion never occurred.
Where Do We Go From Here?
If you operate in a state that is not currently operating under prior authorization, the answer to this question is relatively straightforward, i.e., nothing will change.
If, however, operate in a state that is currently subject to prior authorization, this question is a bit trickier. What we do know is that the actual mechanics of submitting claims will revert to the same process you experienced prior to the implementation of prior authorization. You will submit claims for repetitive patients directly to the Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC), who will likely process them in same manner they process other Medicare claims. In other words, 14 days after the submission of the claim, you will likely receive a remittance notice indicating that the claim has either been paid or denied.
We also know that you will no longer benefit from the protections against post-payment review of these claims. Under the prior authorization model, CMS made clear that it would not audit claims paid based on a valid authorization, except in instances where it could demonstrate that the prior authorization was fraudulently procured.
What We Can Expect from Medicare and its Contractors
What we don’t know is whether the MACs will implement any temporary measures to guard against ongoing over-utilization and/or fraud. To better understand what I mean, put yourself in the position of the MAC. You have empirical evidence (see the chart to the right) that prior authorization has resulted in dramatic reductions in the amount of Medicare dollars paid for dialysis transports. You have further seen little evidence that this reduction in payments has resulted in any serious access to care issues.
The logical conclusion you would draw is that the amounts paid for dialysis prior to the implementation of prior authorization were likely excessive. If so, you might consider some proactive steps to prevent dialysis utilization from increasing back to the levels seen prior to the implementation of prior authorization.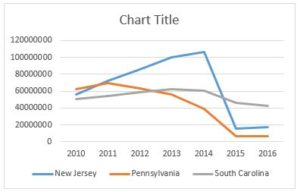
So, it is possible (perhaps even likely) that ambulance suppliers in some of these states may see their MAC elect to implement prepayment reviews for dialysis patients. This could be similar to the process Novitas used for the initial three round trip transports to dialysis.
I also think it is reasonable to expect that the MACs, the Zone Program Integrity Contractors, and the OIG will monitor utilization trends, with an eye towards conducting post-payment reviews on ambulance suppliers that see their dialysis volume increase sharply next year.
Other Potential Impacts
In the previous section, I touched on the steps Medicare and its contractors might take to prevent a return to pre-prior authorization levels of dialysis utilization. In this section, I want to talk about some of the knock-on effects ambulance providers are likely to see.
One of the more interesting changes we saw in the prior authorization regime was a re-balancing of the power dynamic between ambulance suppliers and facilities, i.e., assisted living facilities and skilled nursing homes. Prior to the implementation of prior authorization, that power dynamic was slanted heavily in favor of the facility. By that I mean they could exert tremendous pressure on ambulance suppliers to take marginal patients by ambulance. If you were involved in the industry prior to 2015, you undoubtedly heard an SNF administrator tell you something to the effect of “if your company won’t take the patient by ambulance, I can easily find another company that will.” In competitive markets, that statement was usually accurate.
Under the demonstration project, prior authorization or lack thereof traveled with the patient. What that meant is that if your ambulance company submitted a prior authorization request that was denied, that denial would apply to any other ambulance company that might be interested in taking the patient. As a result, the nursing home could no longer hold the threat of going elsewhere with their business over your head.
Prior authorization also affected the standing policies of dialysis centers. Many free-standing dialysis centers have standing policies that they will not assist in transferring the patient to and from the dialysis treatment chair. This meant that patients that could be transported in a wheelchair van, but who required assistance to transfer out of their wheelchair presented a conundrum. There wouldn’t be medical necessity for the ambulance, but there would be no easy way for you to transfer them into the treatment chair without a second crew member (something most wheelchair van services don’t offer). Under prior authorization, it was easier for the ambulance company to push back, since they knew they wouldn’t be paid for the ambulance. As a result, I have heard that dialysis employees in these states had started to assist patients in transferring.
No really, it’s true…
One potential consequence of the prior authorization going away is that it may shift this power dynamic back to the facilities, with all of the negative consequences that are likely to result.
“Okay, I get what you are saying, but what I really want to know is whether I should loosen our standards for accepting a dialysis patient or not?”
Good question. Unfortunately, not one that permits an easy answer. The implementation of prior authorization shifted the cost-benefit analysis associated with transporting dialysis patients. It was likely that you were going to have a smaller number of patients approved and paid, but you could rest easy that you wouldn’t be at risk of having to return that money years later as the result of a Medicare audit.
The expiration of prior authorization shifts the cost-benefit analysis yet again. It is likely that you have tightened up your criteria for who you accept for dialysis transportation as a result of prior authorization. Loosening those criteria would almost certainly result in an increase in your short-term revenues. However, that would be offset, to some degree, by the increased risk of a Medicare audit.
For that reason, the course of action I have been recommending to people is not to dramatically loosen your standards. Instead, I typically ask whether they currently have patients that they believe do require an ambulance, but who were rejected for prior authorization by the MAC. Most providers respond that they do. Put another way, we are trying to identify the patients that you would feel comfortable defending in an audit. That is the additional population I would target for transportation next year.
Have an issue you would like to see discussed in a future Talking Medicare Blog? Please write to me at bwerfel@aol.com.
CATEGORIES
- AAA HQ
- Ambulance Chaser Blog
- Awards
- Community
- Drugs & Pharma
- Emergency Preparedness
- Events
- Executive
- Field Resources
- Finance
- Global EMS
- Government Affairs
- Human Resources
- Marketing & PR
- Member Advisories
- Member-Only
- News
- Operations
- Patient Care
- Press
- Professional Standards
- Publications
- Quality
- Reimbursement
- Savvik
- Spotlight
- Stars of Life
- Talking Medicare
- Technology
- Uncategorized
- Vehicle Standards
- Workforce Shortage