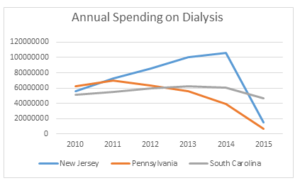
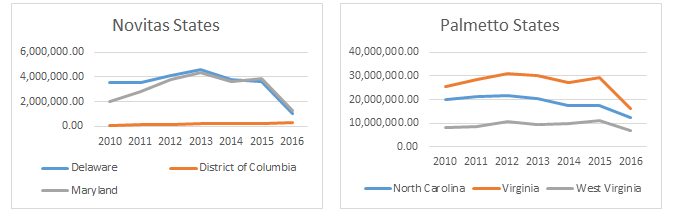
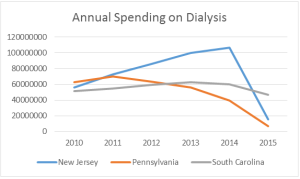
CMS Finalizes Rule to Expand Access to Health Information and Improve the Prior Auth Process
Final rule modernizes the health care system and reduces patient and provider burden by streamlining the prior authorization process
As part of the Biden-Harris Administration’s ongoing commitment to increasing health data exchange and strengthening access to care, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) finalized the CMS Interoperability and Prior Authorization Final Rule (CMS-0057-F) today. The rule sets requirements for Medicare Advantage (MA) organizations, Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) fee-for-service (FFS) programs, Medicaid managed care plans, CHIP managed care entities, and issuers of Qualified Health Plans (QHPs) offered on the Federally-Facilitated Exchanges (FFEs), (collectively “impacted payers”), to improve the electronic exchange of health information and prior authorization processes for medical items and services. Together, these policies will improve prior authorization processes and reduce burden on patients, providers, and payers, resulting in approximately $15 billion of estimated savings over ten years.
“When a doctor says a patient needs a procedure, it is essential that it happens in a timely manner,” said HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra. “Too many Americans are left in limbo, waiting for approval from their insurance company. Today the Biden-Harris Administration is announcing strong action that will shorten these wait times by streamlining and better digitizing the approval process.”
“CMS is committed to breaking down barriers in the health care system to make it easier for doctors and nurses to provide the care that people need to stay healthy,” said CMS Administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure. “Increasing efficiency and enabling health care data to flow freely and securely between patients, providers, and payers and streamlining prior authorization processes supports better health outcomes and a better health care experience for all.”
While prior authorization can help ensure medical care is necessary and appropriate, it can sometimes be an obstacle to necessary patient care when providers must navigate complex and widely varying payer requirements or face long waits for prior authorization decisions. This final rule establishes requirements for certain payers to streamline the prior authorization process and complements the Medicare Advantage requirements finalized in the Contract Year (CY) 2024 MA and Part D final rule, which add continuity of care requirements and reduce disruptions for beneficiaries. Beginning primarily in 2026, impacted payers (not including QHP issuers on the FFEs) will be required to send prior authorization decisions within 72 hours for expedited (i.e., urgent) requests and seven calendar days for standard (i.e., non-urgent) requests for medical items and services. For some payers, this new timeframe for standard requests cuts current decision timeframes in half. The rule also requires all impacted payers to include a specific reason for denying a prior authorization request, which will help facilitate resubmission of the request or an appeal when needed. Finally, impacted payers will be required to publicly report prior authorization metrics, similar to the metrics Medicare FFS already makes available.
The rule also requires impacted payers to implement a Health Level 7 (HL7®) Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR®) Prior Authorization application programming interface (API), which can be used to facilitate a more efficient electronic prior authorization process between providers and payers by automating the end-to-end prior authorization process. Medicare FFS has already implemented an electronic prior authorization API, demonstrating the efficiencies other payers could realize by implementing such an API. Together, these new requirements for the prior authorization process will reduce administrative burden on the healthcare workforce, empower clinicians to spend more time providing direct care to their patients, and prevent avoidable delays in care for patients.
In response to feedback received on multiple rules and extensive stakeholder outreach HHS will be announcing the use of enforcement discretion for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) X12 278 prior authorization transaction standard to further promote efficiency in the prior authorization process. Covered entities that implement an all-FHIR-based Prior Authorization API pursuant to the CMS Interoperability and Prior Authorization Final Rule (CMS-0057-F) who do not use the X12 278 standard as part of their API implementation will not be enforced against under HIPAA Administrative Simplification, thus allowing limited flexibility for covered entities to use a FHIR-only or FHIR and X12 combination API to meet the requirements of the CMS Interoperability and Prior Authorization final rule. Covered entities may also choose to make available an X12-only prior authorization transaction. HHS will continue to evaluate the HIPAA prior authorization transaction standards for future rulemaking.
CMS is also finalizing API requirements to increase health data exchange and foster a more efficient health care system for all. CMS values public input and considered the comments submitted by the public, including patients, providers, and payers, in finalizing the rule. Informed by these public comments, CMS is delaying the dates for compliance with the API policies from generally January 1, 2026, to January 1, 2027. In addition to the Prior Authorization API, beginning January 2027, impacted payers will be required to expand their current Patient Access API to include information about prior authorizations and to implement a Provider Access API that providers can use to retrieve their patients’ claims, encounter, clinical, and prior authorization data. Also informed by public comments on previous payer-to-payer data exchange policies, we are requiring impacted payers to exchange, with a patient’s permission, most of those same data using a Payer-to-Payer FHIR API when a patient moves between payers or has multiple concurrent payers.
Finally, the rule also adds a new Electronic Prior Authorization measure for eligible clinicians under the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) Promoting Interoperability performance category and eligible hospitals and critical access hospitals (CAHs) in the Medicare Promoting Interoperability Program to report their use of payers’ Prior Authorization APIs to submit an electronic prior authorization request. Together, these policies will help to create a more efficient prior authorization process and support better access to health information and timely, high-quality care.
The final rule is available to review here: https://www.cms.gov/files/document/cms-0057-f.pdf.
The fact sheet for this final rule is available here: https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/cms-interoperability-and-prior-authorization-final-rule-cms-0057-f.
###