CMS Announces Comment Period for National Expansion of Prior Authorization Process
On October 29, 2019, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) posted a notice in the Federal Register announcing an opportunity for the public to provide comments on the proposed national expansion of the prior authorization process for repetitive, scheduled non-emergent ground ambulance transportation. CMS refers to this process as its “RSNAT Prior Authorization Model.” The CMS Notice can be viewed in its entirety at: https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2019-10-29/pdf/2019-23584.pdf.
Under the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, federal agencies are required to publish a notice in the Federal Register concerning each proposed collection of information, and to allow 60 days for the public to comment on the proposed action. Interested parties are encouraged to provide comments regarding the agency’s burden estimates and other aspects of the proposed collection of information, including the necessity and utility of the proposed information for the proper performance of the agency’s functions, and ways in which the collection of such information can be enhanced.
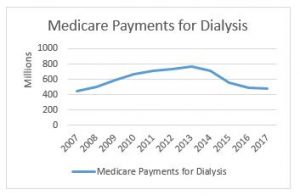
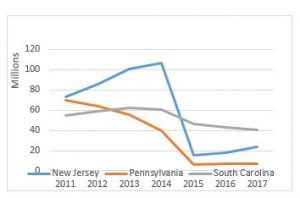
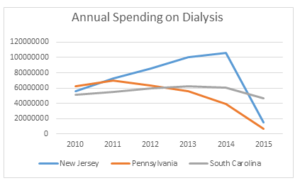
In this instance, CMS is indicating that it is pursuing approval to potentially expand the existing RSNAT Prior Authorization Model nationwide. Currently, the RSNAT Prior Authorization Model is in place in 8 states (DE, MD, NJ, NC, PA, SC, VA, and WV) and the District of Columbia. National expansion is contingent upon CMS’ determination that certain expansion criteria have been met. CMS is indicating that if the decision is made to expand the program, such expansion may occur in multiple phases. CMS intends to use the information collected pursuant to this notice to determine the proper payment for repetitive scheduled non-emergent ambulance transportation.
In plain English, CMS is soliciting comments from stakeholders as to the efficacy of the current process, including whether the existing paperwork requirements are sufficient to ensure that approved patients meet the medical necessity requirements for an ambulance. CMS is also seeking suggestions for how to best expand the program nationally, e.g., whether it makes sense to expand the program in phases, etc.
The AAA Medicare Regulatory Committee has been monitoring the current model for several years. As a result, the AAA is in a good position to provide constructive feedback to CMS regarding the potential national expansion of the RSNAT Prior Authorization Model. These suggestions will be included in the AAA’s comment letter. The AAA also encourages members to offer their own comments. The AAA anticipates providing members with a sample comment letter in early December that members can use to submit their own comments.
To be considered, comments must be submitted no later than 5 p.m. on December 30, 2019. Comments may be submitted electronically by going to: http://www.regulations.gov. Commenters would then need to click the link for “Comment or Submission,” and follow the instructions from there. Comments may also be submitted by regular mail to the following address: CMS, Office of Strategic Operations and Regulatory Affairs, Division of Regulations Development, Attention: Document Identifier: CMS-10708, Room C4-26-05, 7500 Security Boulevard, Baltimore, Maryland 21244-1850.