Talking Medicare: CMS Implements Further Dialysis Cuts
Talking Medicare: CMS Implements Further Cuts in Reimbursement for Dialysis Services; Medicare Payment Data Shows Continued Reduction in Overall Spending on Dialysis Transports, but Net Increase in Dialysis Payments in Prior Authorization States
On October 1, 2018, CMS implemented an additional thirteen (13%) cut in reimbursement for non-emergency BLS transports to and from dialysis. This cut in reimbursement was mandated by Section 53108 of the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018. This on top of a ten (10%) cut in reimbursement for dialysis transports that went into effect on October 1, 2013. As a result, BLS non-emergency ambulance transports to and from dialysis that occur on or after October 1, 2018 will be reimbursed at 77% of the applicable Medicare allowable.
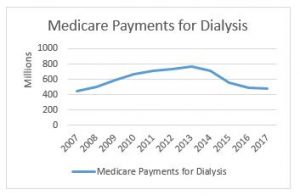
In related news, CMS has released its national payment data for calendar year 2017. This data shows a continued reduction in total Medicare payments for dialysis transports. Medicare paid $477.7 million on dialysis transports in 2017, down from $488.9 million in 2016. This continues a downward trend that has seen total payments decline from a high of more than $750 million in 2013 (see accompanying chart to the right). Not coincidentally, it was in 2013 that our industry saw its first reduction in Medicare’s payments for dialysis transports.
The payment reduction is partially the result of the reduction in the amounts paid for dialysis services. However, it is also reflective of an overall decline in the number of approved dialysis transports. For this, we can look primarily to the impact of a four-year demonstration project that requires prior authorization of dialysis transports in 8 states and the District of Columbia.
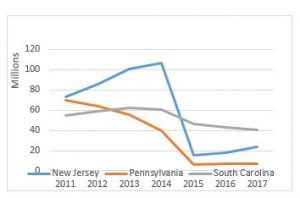
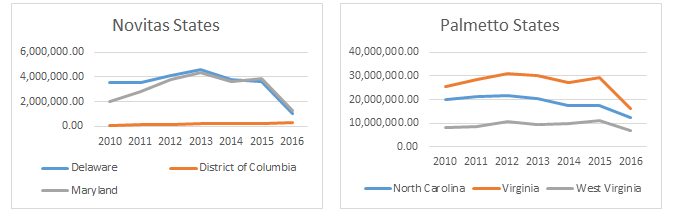
As a reminder, the original prior authorization states were selected based on higher-than-average utilization rates and high rates of improper payment for these services. In particular, the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) had singled out these states as having higher-than-average utilization of dialysis transports in a June 2013 report to Congress. The chart below shows total spending on dialysis in those states in the years immediately preceding the implementation of the prior authorization project up through 2017, the third year of the demonstration project. While the three states had very different trajectories prior to 2015, each showed a significant decrease in total payments for dialysis under the demonstration project.
However, it is the trajectory of these changes that I want to discuss in this month’s blog. In previous blogs, I discussed the impact of the particular Medicare Administrative Contractor on the outcomes under prior authorization. Specifically, I noted that, while dialysis payments dropped in each state, the decline was far more dramatic in the states administered by Novitas Solutions (NJ, PA) than in the South Carolina, which was administered by Palmetto GBA. This trend continued in the second year of the program, which saw prior authorization expanded into five additional states and the District of Columbia. Those states administered by Novitas (DE, MD) saw far greater declines than the states administered by Palmetto (NC, VA, WV).
Given these declines, the data from the third year is somewhat surprising. The states administered by Palmetto continued to see declines in total dialysis payments, with the only exception being West Virginia. However, in the states administered by Novitas, we saw total dialysis payments increase, particularly in New Jersey, which saw nearly a 33% increase in total dialysis payments.
Three years into the prior authorization program, it is starting to become clear that the two MACs have approached the problem of overutilization of dialysis transports using two different approaches. Palmetto appears to have adopted a slow-and-steady approach, with total payments declining in a consistent manner year after year. By contrast, Novitas adopted more of a “shock the system” approach, where it rejected nearly all dialysis transports in the first year, and has adopted a somewhat more lenient approach in subsequent years.
Key Takeaways
Last year, I wrote that two years of data under the prior authorization program permitted two conclusions: (1) the implementation of a prior authorization process in a state will undoubtedly result in an overall decrease in the total payments for dialysis within that state and (2) the size of that reduction appears to be highly dependent on the Medicare contractor.
With an additional year of data, I think both conclusions remain valid, although I would revise the second to suggest that the initial reduction has more to do with the Medicare contractor. The evidence from the third year of the program suggests that the trends tend to equalize after the first few years. It is also possible that Novitas felt a more aggressive approach was needed in the first few years to address evidence of widespread dialysis overutilization in the Philadelphia metropolitan area.
This has potential implications beyond the demonstration project, as CMS looks towards a possible national expansion of the program. Among other issues, it suggests that the AAA must continue its efforts to work with CMS and its contractors on developing more uniform standards for coverage of this patient population.
What the AAA is Doing
The AAA continues to work on legislation that would restructure this cut to dialysis transport reimbursement. The AAA strongly supports the NEATSA Act (H.R.6269) introduced by Congressman LaHood (R-IL) and Congresswoman Sewell (D-AL) that would restructure the offset so that a majority of the additional reduction would be focused on those ambulance service agencies in which 50% or more of their volume are repetitive BLS nonemergency transports. AAA members and the AAA are working to get a Senate companion bill introduced shortly. The goal of this legislation would be to have the restructured offset go into effect as soon as possible. Thank you to the dozens of AAA members who have already contacted their members of Congress voicing their support for this critical legislation.
Have an issue you would like to see discussed in a future Talking Medicare blog? Please write to me at bwerfel@aol.com